Depth First Search
Given a graph G = (V, E), a depth-first search (DFS) is a graph traversal algorithm that starts at a given vertex v of G, and explores as far as possible along each branch before backtracking.
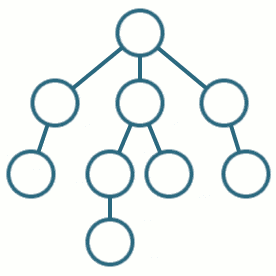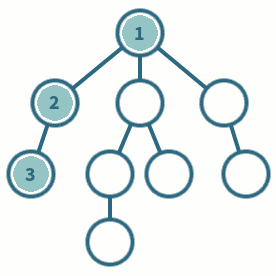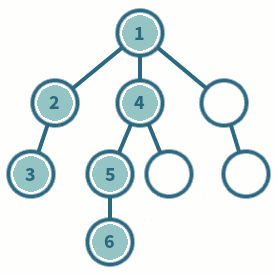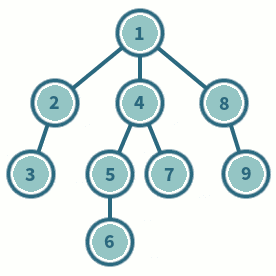
DFS is actually a general search heuristic, not only applied for graph traversal, but also for other problems. As we have shown in breadth-first-search, DFS can also be used to find the solution of subset sum.
Subset Sum
Given a set of integers and a target value, find if there is a subset of the given set with sum equal to the given target.
Example
- Input:
numbers = [3, 8, 10, 6, 7],target = 15 - Output:
True - Explanation: The subset
{8, 7}has sum15.
Algorithm
The basic idea is to solve the problem by brute force, i.e., enumerate all the subsets and check if the sum of the subset is equal to the target.
Example
Input: numbers = [3, 8, 10, 6, 7], target = 15
The search begins with the first number 3, producing the sequence [3], [3, 8], [3, 8, 10], [3, 8, 10, 6], [3, 8, 10, 6, 7]. It then checks the sum of [3, 8, 10, 6, 7]. Since it does not equal the target, the algorithm backtracks to the previous state [3, 8, 10, 6] and checks the sum again (still not equal to the target). Next, it backtracks to [3, 8, 10] and explores deeper with [3, 8, 10, 7]. This process continues until it finds a subset whose sum equals the target.
Code
The depth first search is often implemented in a recursive way.
Define a recursive function dfs(subset, index), in which subset represents the current set of numbers, index is the current index of the given numbers set.
There are 4 cases to consider:
- If the sum of the current set of numbers is equal to the target, return the current set of numbers.
- If the sum of the current set of numbers is greater than the target return
None. - If the index exceeds the length of the given
numbersset, returnNone. - Otherwise, we have two choices:
- Add the current number to the current set of numbers, and continue the search with the new set of numbers.
- Do not add the current number to the current set of numbers, and continue the search with the new set of numbers.
def subset_sum_dfs(numbers, target):
def dfs(subset, index):
current_sum = sum(subset)
if current_sum == target:
return subset
if current_sum > target:
return None
if index == len(numbers):
return None
return dfs(subset + [numbers[index]], index + 1) or dfs(subset, index + 1)
return dfs([], 0)